Lack of Reporting
Bacterial infections range in severity, some such as an ear infection do not normally require hospitalization. However, others such as tuberculosis pose a threat to populations and hospitals are required to report the infection. The many infections that do not need to be treated and patients do not go to the hospital for are not reported, so there are no projections on the number of bacterial infections per year. Consider that E. coli, salmonella, gonorrhea, meningitis, staph infections, strep throat, ear infections, pneumonia and many others are caused by bacteria. Many of these bacterium are prone to becoming antibiotic resistant, and there have been strains found in almost all of these infections.


This graphic shows the current economic effect that antibiotic resistance has on the United States.
This graph shows that the projected amount of antimicrobial resistant related deaths will total 10 million by the year 2050. This is higher than Cancer (8.2 million as of now).
Problem Statement: When an antibiotic is used, bacteria that can resist that particular antibiotic will not be killed off, which is the intended purpose of antibiotic usage. The remaining bacteria creates multidrug resistant strains, causing an infection that can not be stopped with today’s antibiotic technology. These infections threaten global health, and the trend of antibiotic resistance continues to climb at an alarming rate.
Economic Toll
Current statistics state antibiotic resistant infections lower current world GDP by 1.4-1.6% per year. This percentage will only increase, the economic burden is significant already.
Creation of New Threats
Also, antibiotic resistance poses a huge threat to other healthcare advancements. This is because antibiotic infections combined with other infections (such as tuberculosis) creates a more rapid disease progression. This makes the infected person less likely to overcome the disease with two illnesses affecting them. Also, the new, resistant, strain is now spread to the public.
Application of the Projected Trends
To truly comprehend the toll that antibiotics takes, one can observe the common hip replacement. Currently, antibiotics are heavily relied on for this simple procedure. Without the antibiotics we use now, 30-40% of patients undergoing this procedure would develop infections. About 30% of those infections would prove fatal. Consider how many people undergo hip replacements per year in the US: there are 51.4 million hip replacements. Without antibiotics, 20.56 million people would get infections, and 6.168 million people would die. This means for hip replacements alone, 6.168 million people would die per year of antibiotic resistant infections.
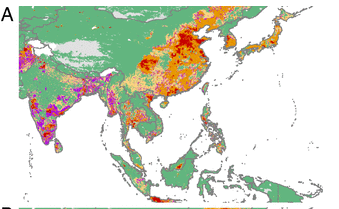
Increasing Trends
Resistance is only growing, the below graph shows Asia's antibiotic consumption in chicken. By 2030, chicken consumption is project to grow 129%. In India alone, consumption rates are expected to grow 312% by 2030.
Overuse
Antibiotic resistance is possible with most bacterial infections. The listed infections that are already killing people with working antibiotics help, soon even the most modern antibiotics will not work. The trend of overuse of antibiotics, in the United States, is undeniable. Also, antibiotic therapy is prescribed incorrectly 30-50% of the time.

Antimicrobial consumption in chickens in 2010. Purple indicates new areas where antimicrobial consumption will exceed 30 kg per 10 km2 by 2030.